Introduction and History
Among the entertainment service companies over the world, Lucasfilm Ltd.LLC is an innovator in the field of films’ visual effects, sound effects and computer animation. Lucasfilm was founded by George Lucas in San Rafael, California in 1971(Lucasfilm, 2018). In 2005, Lucas spent $350 million moving their headquarters including Lucasfilm, Industrial Light & Magic (ILM) and most of the operations to the Letterman Digital Arts Center at the Presidio in San Francisco where the headquarters locate at present (Waxman, 2005). Lucasfilm owns copyrights of films, TV series, websites and games in which Star Wars and Indiana Jones (franchises) are well known to audiences. There are many recent works that were successful. The Star Wars: The Force Awakens (2015) received five Academy Awards nominations including Visual Effects and Sound Mixing (Star Wars, 2015). Besides, the Star Wars: The Last Jedi (2017) received four Academy Awards including Visual Effects and Original Score (Star Wars, 2017).

George Walton Lucas, the founder of Lucasfilm, is a filmmaker, writer and producer who is estimated a net worth of $5.1 billion today and he was the CEO and chairman before selling Lucasfilm to The Walt Disney Company in 2012 for $4.05 billion which made Lucas the second-largest non-institutional shareholder of Disney (Krantz, Snider, Cava, & Alexander, 2012). Kathleen Kennedy became the president and brand manager for Star Wars and Lynwen Brennan became executive vice president and general manager. At the same time, Disney acquired all the ownership of Lucasfilm including visual effects, video games, animation, technology and portfolios (Star Wars, 2012).

“Dreams are extremely important. You can’t do it unless you imagine it.”
-George Lucas
Company Structure and Business Model
By 2015, Lucasfilm had a whole of 2000 employees within 5 campuses around the world: San Francisco, Vancouver, London, Singapore and Skywalker Ranch (Michal, 2015). Different divisions in Lucasfilm operate various kinds of works.
Industrial Light & Magic (ILM), leading by Lynwen Brennan, is centered for visual effects and sound productions. In 2016, ILM won the Visionary Vanguard Award at the 27th annual PGA Awards ceremony for their visual effects and revolutionized story telling (Industrial Light & Magic, 2018).
“ILM’s dedication to advancing the creative possibilities of film has inspired the imaginations of storytellers worldwide and provided the tools to transport audiences to richly immersive new worlds.”
-Producers Guild Awards Co-Chairs Michael DeLuca and Jennifer Todd
Although Star Wars is their primary product, ILM also provides technical services to other film companies and studios like Regency Enterprises and Marvel Studios. Visual Effects (VFX) Academy Award nominee that ILM received for their film services included Doctor Strange (2016), The Revenant (2015) and Deepwater Horizon (2016). Rango (2011) won the Best Animated Feature Film of the Year of Academy Award. One of the fact that made ILM different with other VFX companies is that ILM has their own technology innovation when producing films. According to an article on The Walt Disney Company’s website, ILM VFX team used a procedural rigging system named BlockParty in the Ant-Man and The Wasp to help creating “digital” characters with motion-capture and detail creating which improving the productivity of film producing (The Walt Disney Company, 2018).
ILM x LAB is one of the studios launched by Industrial Light & Magic (ILM) in 2015 for creating AR, VR and visual effects and they just announced that there will be a VR series called Vader Immortal: A Star Wars VR Series coming in 2019 (ILM x LAB, 2018).
Skywalker Sound locates in Skywalker Ranch offers sound-related services such as sound design, re-recording mixing and music scoring. They did sound production for various film production companies like Amblin Entertainment, ImageMovers and Baozou Manhua. There are many subsidiaries of Lucasfilm including LucasArts and Lucasfilm Animation Ltd. LLC which were also acquired by The Walt Disney Company in 2012 but Disney shut LucasArts down in 2013 and cancelled their projects as well (Schreier, 2013).
Revenue Model
The largest revenue Lucasfilm made was on Star Wars films. There were four films distributed by Walt Disney Studios Motion Pictures after Lucasfilm was acquired. According to Box Office Mojo, Star Wars: The Force Awakens received a box office of $2.068 billion while the budget was $250 million (Box Office Mojo, 2015). Rogue One: A Star Wars Story got a box office of $1.313 billion with $200 million budget (Box office Mojo, 2016) and Star Wars: The Last Jedi got a $1.333 billion of box office with budget of $200 million (Box Office Mojo, 2017). These three films already brought in over $4 billion to The Walt Disney Company that Lucasfilm was bought for. Besides, the revenues of Star Wars’ home-video release, toys, movie licensing, Star Wars TV shows, Star Wars theme park and other products were not in count (Rodriguez, 2018).
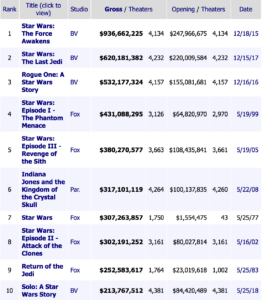
According to Disney’s Fiscal Year 2013 Annual Financial Report and Shareholder Letter, Lucasfilm’s special effect business made contributions to the revenue increase in television and SVOD (TV/SVOD) in 2013. What’s more, the licensing and publishing is also a source of revenue for Lucasfilm which is also one of the reason that cause the 10% revenue increase in 2013 including 8% of licensing and 2% of publishing. Other revenue sources include Lucas film’s interactive games business and other Star Wars product sales and activities (The Walt Disney Company, 2014).
“Intangible assets primarily consist of intellectual property based on the Star Wars franchise with an estimated useful life of approximately 40 years. The goodwill reflects the value to Disney from leveraging Lucasfilm intellectual property across our distribution channels, taking advantage of Disney’s established global reach” (The Walt Disney Company, 2014).
Star Wars: Episode IX is scheduled to come in 2019. At the same time, Lucasfilm still keeps creating and exploring more technologies in many fields. Lucasfilm and ILM just released the the MaterialX v1.36 Library for computer graphics which is an open standard to help transferring rich materials between applications and renders (Industrial Light & Magic, 2018).
Sources:
Lucasfilm Company History | Lucasfilm Ltd. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.lucasfilm.com/who-we-are/our-story/
Waxman, S. (2005, July 20). Lucas’s New Headquarters Give Bay Area Film a Lift. The New York Times. Retrieved from https://www.nytimes.com/2005/07/20/movies/lucass-new-headquarters-give-bay-area-film-a-lift.html
Krantz, M., Snider, M., Cava, M. D., & Alexander, B. (2012, October 31). Disney buys Lucasfilm for $4 billion. Retrieved from https://www.usatoday.com/story/money/business/2012/10/30/disney-star-wars-lucasfilm/1669739/
Star Wars. (2012, October 30). New Star Wars Movies Announced as Disney Enters Agreement to Acquire Lucasfilm Ltd. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.starwars.com/news/new-star-wars-movies-announced-as-disney-enters-agreement-to-acquire-lucasfilm-ltd
Michal, L. (2015, September 10). How the Star Wars producer went from secretary to studio boss. Retrieved from http://fortune.com/2015/09/10/kathleen-kennedy-lucasfilm-star-wars/
ILM x LAB. Vader Immortal: A Star Wars VR Series and Trailer Revealed. (2018, September 26). Retrieved from https://www.ilmxlab.com/news/vader-immortal-a-star-wars-vr-series-and-trailer-revealed/
Box Office Mojo. Star Wars: The Force Awakens (2015). (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.boxofficemojo.com/movies/?id=starwars7.htm
Box Office Mojo. Star Wars: The Last Jedi (2017). (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.boxofficemojo.com/movies/?id=starwars8.htm
Star Wars. Star Wars: The Force Awakens Receives 5 Oscar Nominations. (2016, January 14). Retrieved from https://www.starwars.com/news/star-wars-the-force-awakens-receives-5-oscar-nominations
Star Wars. Star Wars: The Last Jedi Receives 4 Oscar Nominations. (2018, January 23). Retrieved from https://www.starwars.com/news/star-wars-the-last-jedi-receives-4-oscar-nominations
Industrial Light & Magic. (2018). Leadership. Retrieved from https://www.ilm.com/leadership/
Skywalker Sound. Sound Design, Mixing, and More Services. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.skysound.com/services/
Schreier, J. (2013, April 04). Disney Shuts Down LucasArts, Cancels Star Wars 1313 And Star Wars: First Assault. Retrieved from https://kotaku.com/disney-shuts-down-lucasarts-468473749
Industrial Light & Magic. (2018). PGA Vanguard Visionary Awards. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.ilm.com/awards/pga-vanguard-visionary-award/
The Walt Disney Company. Industrial Light & Magic Brings Award-Winning Innovation to Marvel Studios’ ‘Ant-Man and The Wasp’. (2018, July 11). Retrieved from https://www.thewaltdisneycompany.com/industrial-light-magic-brings-award-winning-innovation-to-marvel-studios-ant-man-and-the-wasp/
Rodriguez, A. (2018, January 02). Disney’s Star Wars films have earned more than Lucasfim was bought for. Retrieved from https://qz.com/1169393/disneys-star-wars-films-have-earned-more-than-lucasfim-was-bought-for/
The Walt Disney Company. (2014). Fiscal Year 2013 Annual Financial Report And Shareholder Letter. Way Back Machine. Retrieved from https://web.archive.org/web/20140221125252/http://thewaltdisneycompany.com/sites/default/files/reports/10k-wrap-2013.pdf
Industrial Light & Magic. (2018). MaterialX Open Sourced, Retrieved from https://www.ilm.com/leadership/
